![]()
迭代器模式
迭代器设计模式 - Refactoring.Guru
设计模式| 迭代器模式及典型应用| 小旋锋
目的
在不暴露集合底层表现形式 (列表、 栈和树等) 的情况下遍历集合中所有的元素。
主要思想
将集合的遍历行为抽取为单独的迭代器对象。
结构
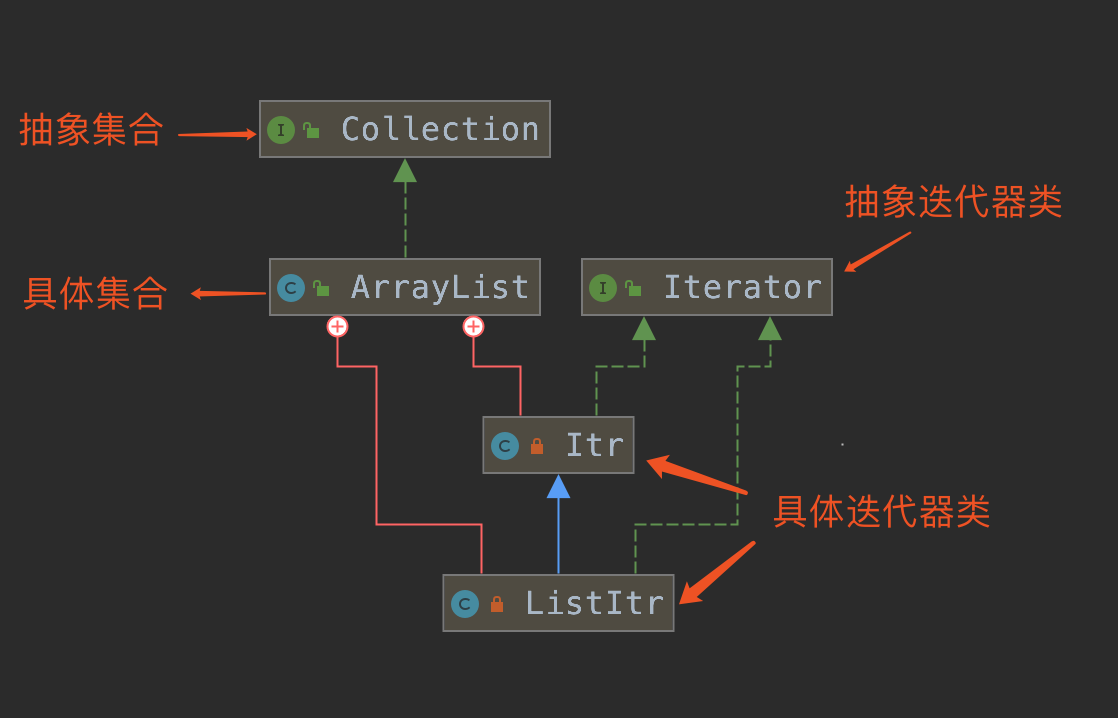
- 抽象迭代器(Iterator)
- 具体迭代器(Concrete Iterators)
- 抽象集合(Collection)
- 具体集合(Concrete Collections)
简单示例
学生报数
抽象迭代器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public interface StudentIterator {
boolean hashNext();
Student next();
int getPosition();
}
|
具体迭代器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| public class ConcreteStudentIterator implements StudentIterator {
private Student[] students;
private int position = 0;
public ConcreteStudentIterator(Student[] students) {
this.students = students;
}
@Override
public int getPosition() {
return position;
}
@Override
public boolean hashNext() {
return position < students.length;
}
@Override
public Student next() {
return students[position++];
}
}
|
抽象集合
1
2
3
4
| public abstract class StudentCollection {
abstract StudentIterator createIterator();
}
|
具体集合
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public class ConcreteStudentCollection extends StudentCollection {
private Student[] students;
public ConcreteStudentCollection(Student[] students) {
this.students = students;
}
@Override
StudentIterator createIterator() {
return new ConcreteStudentIterator(students);
}
}
|
客户端使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| public static void main(String[] args) {
StudentCollection studentCollection = new ConcreteStudentCollection(new Student[]{new Student("张三"), new Student("李四")});
StudentIterator iterator = studentCollection.createIterator();
while (iterator.hashNext()) {
Student student = iterator.next();
System.out.println("我是" + iterator.getPosition() + "号:" + student.getName());
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
| 我是1号:张三
我是2号:李四
Process finished with exit code 0
|
典型应用
Java 集合
![]()